Are you trying to run queries from the MySQL Command Line ?
This guide will help you.
The MySQL command line tool allows you to run queries and administer databases from the command line. It lets you send SQL queries directly to the MySQL server and output the results in text format. It is a quick and easy way to test your MySQL installation.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to perform SQL related queries.
In this context, we shall look into how to execute queries from the MySQL Command Line .
More information about MySQL command line?
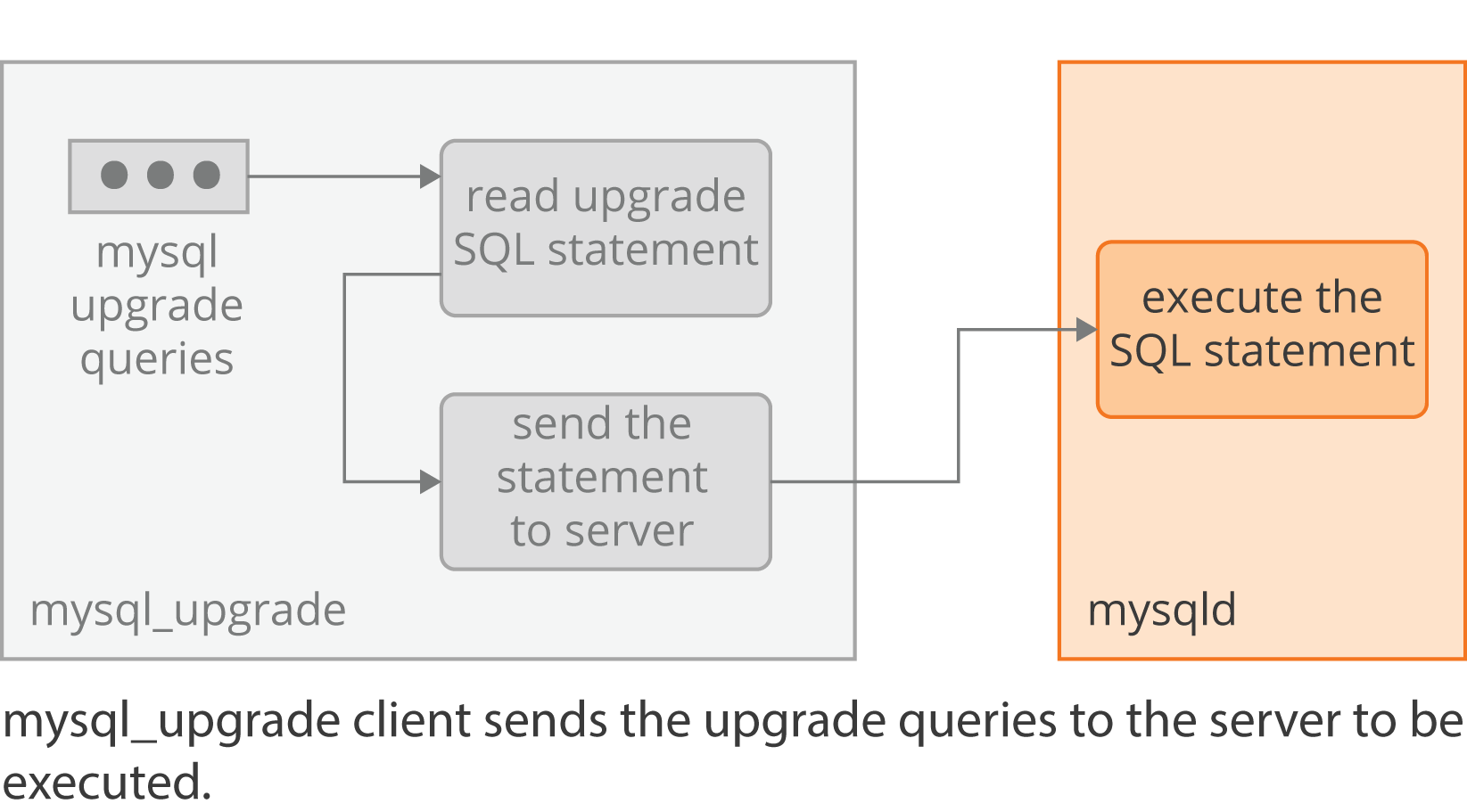
mysql is a simple SQL shell with input line editing capabilities. It supports interactive and noninteractive use. When used interactively, query results are presented in an ASCII-table format.
To start MySQL from command line:
1. Select the option to run MySQL as a service.
2. Launch the MySQL Command-Line Client.
3. To launch the client, enter the following command in a Command Prompt window: mysql -u root -p .
The -p option is needed only if a root password is defined for MySQL.
How to execute select queries from MySQL command line ?
After logging into a database with the MySQL command line tool, you can run queries by simply typing them in at the command prompt. The query will not be executed until you either enter ; g or G and then press the <enter> key. This allows you to write a query across several lines and then execute it at the end by entering ; and then <enter>.
For example, if we have a table which stores country codes and names, we can query the data like so:
mysql> select country_code, name from countries order by name limit 0, 5;The result set would then be displayed, showing something like below. It will be displayed in this horizontal format whether you use ; or g to execute the query.
You will see an output such as this:
+--------------+----------------+
| country_code | name |
+--------------+----------------+
| AF | AFGHANISTAN |
| AL | ALBANIA |
| DZ | ALGERIA |
| AS | AMERICAN SAMOA |
| AD | ANDORRA |
+--------------+----------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)How to display the result set vertically from MySQL command line ?
In a cases where your query result contains a lot of columns then the data will wrap if it is too long. This can make it difficult to find the information you are looking for because the output can be quite messy.
The MySQL command line tool allows you to show the output vertically which overcomes this issue, using G to execute the query.
Therefore, executing the same query as above with G:
mysql> select country_code, name from countries order by name limit 0, 5GThen the corresponding output will look like this:
*************************** 1. row ***************************
country_code: AF
name: AFGHANISTAN
*************************** 2. row ***************************
country_code: AL
name: ALBANIA
*************************** 3. row ***************************
country_code: DZ
name: ALGERIA
*************************** 4. row ***************************
country_code: AS
name: AMERICAN SAMOA
*************************** 5. row ***************************
country_code: AD
name: ANDORRA
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)How to use MySQL Command Line Tool History ?
The MySQL command line tool keeps a history of the SQL queries you have run. On a Linux/Unix machine this is stored in your home directory in the file .mysql_history. When you are in the MySQL command line tool, you can go back through this history by using the up and down arrow keys.
The up arrow moves you back through the history and the down arrow forward through the history again.
How to clear the current query from MySQL command line ?
If you navigate through the history but decide you don’t want to run any of the queries, or if you’ve typed in a query that you decide you don’t want to run after all, you don’t need to use the backspace key to clear the query. Enter c and then press <enter> and the query will be cleared without running.
[Need urgent support to fix any SQL error? We are available to help you today. ]
Conclusion
This article will guide you on how to run queries from the 3MySQL command line. The MySQL #Command Line Tool is a useful way to run #queries from the command line. It’s easy to run select queries and display the results in either a horizontal or vertical format, and the queries run are kept in a history file which you can navigate through.
If you don't want to run a particular query after all you can use the c command to clear it.
The most common way to get a list of the MySQL #databases is by using the mysql client to connect to the MySQL server and run the SHOW DATABASES command. If you haven't set a password for your MySQL user you can omit the -p switch.
To Connect to a MySQL Database:
1. Click Services tab.
2. Expand the Drivers node from the Database Explorer.
3. Enter User Name and Password.
4. Click OK to accept the credentials.
5. Click OK to accept the default schema.
6. Right-click the MySQL Database #URL in the Services window.
This article will guide you on how to run queries from the 3MySQL command line. The MySQL #Command Line Tool is a useful way to run #queries from the command line. It’s easy to run select queries and display the results in either a horizontal or vertical format, and the queries run are kept in a history file which you can navigate through.
If you don't want to run a particular query after all you can use the c command to clear it.
The most common way to get a list of the MySQL #databases is by using the mysql client to connect to the MySQL server and run the SHOW DATABASES command. If you haven't set a password for your MySQL user you can omit the -p switch.
To Connect to a MySQL Database:
1. Click Services tab.
2. Expand the Drivers node from the Database Explorer.
3. Enter User Name and Password.
4. Click OK to accept the credentials.
5. Click OK to accept the default schema.
6. Right-click the MySQL Database #URL in the Services window.