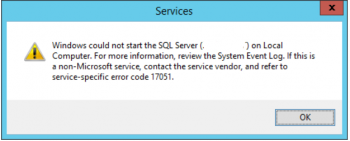
SQL error 825 indicates that the read operation had to be reissued at least one time, and indicates a major problem with the disk hardware.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is the standard and most widely used programming language for relational databases. It is used to manage and organize data in all sorts of systems in which various data relationships exist.
Error 825 is also referred to as the read-retry warning, however the condition is for both read and write operations.
This error lets you know that a retry of the operation was needed and how many times SQL Server had to retry the attempt before it was successful.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to resolve SQL related errors.
In this context, we shall look into methods to fix this SQL error.
Nature of SQL error 825 ?
As earlier stated, The error 825 is also called as the read-retry warning.
This error tells a retry operation was needed. Also, it tells how many times SQL Server had to retry the attempt before it was successful.
This message doesn't mention that there is a SQL server problem. Instead, it indicates a larger problem with the disk subsystem which may lead to data loss or database corruption if it is not resolved.
Here is a complete error message:
~~
Msg 825, Level 10, State 2, Line 1.
A read of the file ‘D:\SQLskills\TestReadRetry.mdf’ at offset 0×0000017653C000 succeeded after failing 2 time(s) with error: incorrect checksum (expected: 0×4a224f20; actual: 0×2216ee12). Additional messages in the SQL Server error log and system event log may provide more detail. This error condition threatens database integrity and must be corrected. Complete a full database consistency check (DBCC CHECKDB). This error can be caused by many factors; for more information, see SQL Server Books Online.
~~Method to fix SQL error 825 ?
In order to resolve this error, you can try the tips provided below.
1. Check the error log to find clues that explain the problem.
2. This error mainly relates to disk, the disk controllers, array cards, or disk drivers. So make sure to check the disk system.
3. Contact the disk manufacturer for the latest utilities for checking the status of your disk system. Also, check for the latest driver updates.
4. Try moving all files into a new physical drive(on a new hardware LUN).
Below are the steps to move all files to a new physical drive.
i. First, add a new Drive (for example, X)
ii. Secondly, create the same folder structure as on the D drive.
iii. Then stop the SQL Service.
iv. Now move files from D drive to X drive.
v. Swap the Drive letters (D > Y, X > D, Y > X)
vi. Finally, start the SQL Service. (you might get some permission errors so make sure to set permissions accordingly).
[Need urgent further assistance in fixing SQL errors? – We're available 24*7. ]
Conclusion
This article will guide you on methods to resolve SQL error 825 which indicates a major disk problem and not a SQL server problem.
The connection to #SQL server cannot be established or is no longer usable. There can be various causes of this #error. The most common causes are that Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server has stopped or the connection to SQL #Server is not configured correctly.
To find SQL errors:
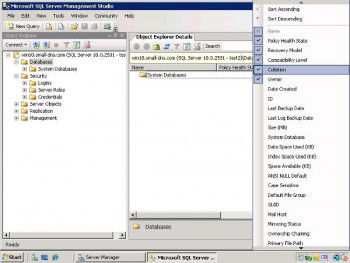
i. In SQL Server Management Studio, select Object Explorer.
ii. In Object Explorer, connect to an instance of SQL Server, and then expand that instance.
iii. Find and expand the Management section (assuming you have permissions to see it).
iv. Right-click SQL Server Logs, select View, and then choose SQL Server Log.
Every SQL Server #database has a transaction log that records all transactions and the database modifications made by each transaction. The transaction log is a critical component of the database. If there is a system failure, you will need that log to bring your database back to a consistent state.
To get SQL query history in SQL Server:
1. In Object Explorer, connect to an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine, and then expand that instance.
2. Expand SQL Server Agent, and then expand Jobs.
3. Right-click a job, and then click View History.
4. In the Log File Viewer, view the job history.
5. To update the job history, click Refresh.
This article will guide you on methods to resolve SQL error 825 which indicates a major disk problem and not a SQL server problem.
The connection to #SQL server cannot be established or is no longer usable. There can be various causes of this #error. The most common causes are that Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server has stopped or the connection to SQL #Server is not configured correctly.
To find SQL errors:
i. In SQL Server Management Studio, select Object Explorer.
ii. In Object Explorer, connect to an instance of SQL Server, and then expand that instance.
iii. Find and expand the Management section (assuming you have permissions to see it).
iv. Right-click SQL Server Logs, select View, and then choose SQL Server Log.
Every SQL Server #database has a transaction log that records all transactions and the database modifications made by each transaction. The transaction log is a critical component of the database. If there is a system failure, you will need that log to bring your database back to a consistent state.
To get SQL query history in SQL Server:
1. In Object Explorer, connect to an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine, and then expand that instance.
2. Expand SQL Server Agent, and then expand Jobs.
3. Right-click a job, and then click View History.
4. In the Log File Viewer, view the job history.
5. To update the job history, click Refresh.