Packet drop on bond0 occurs due to many reasons such as network congestion, problems with network hardware, security threats, and so on.
Data is transferred across the network as small units called packets. Sometimes these packets won't reach the destination and are called packet loss.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to fix interface errors.
What is this bond0?
This is the first question to be discussed before anything.
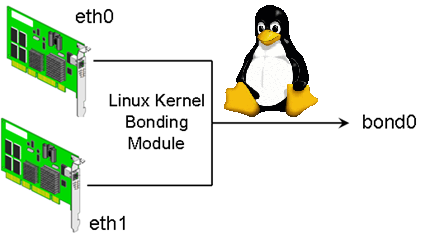
In Linux, in order to connect more than one network interfaces into a single interface, a special kernel module named bonding is used.
Here, two or more network interfaces can be connected into a single logical "bonded" interface.
And, the behavior of these bonded interfaces depends on the mode. These modes include: Mode0, mode1, mode2, etc.
Today, let's see how our Experts deal with problems with the bond0 interface.
How we find and fix Packet Drop On bond0?
Recently, one of our customers having IPTV servers approached us saying that the portal loading is very slow.
So, we checked in detail and found that there were some packets drop in one of his interfaces.
Some deep checks revealed that the problem was with his bond0 interface.
He was having a bond0 interface and on further checking, we found that the bonding mode employed here is
Bonding Mode: IEEE 802.3ad Dynamic link aggregation.
Here, the LACP – Link Aggregation Control Protocol balances outgoing traffic across the active ports,
on the basis of hashed protocol header information and accepts incoming traffic from any active port.
Other interfaces have no such drops.
Finally, we confirmed that the problem is with the hardware, as our Engineers did all other possible checks.
Hence, we passed these details we found and asked the customer to contact DC to check the hardware,
Later, the customer informed that DC replaced the cable as it was broken.
This fixed the customer's problem.
Our Experts, always put their full effort into finding the fix for our customer's problems.
[Having trouble with your Interface – We can help you. ]
Conclusion
This article will help to fix packet drop on bond0. Here, you will learn more about packet loss.
In Linux, in order to connect more than one network interfaces into a single interface, a special kernel module named bonding is used.
Here, two or more network interfaces can be connected into a single logical “bonded” interface.
This article will help to fix packet drop on bond0. Here, you will learn more about packet loss.
In Linux, in order to connect more than one network interfaces into a single interface, a special kernel module named bonding is used.
Here, two or more network interfaces can be connected into a single logical “bonded” interface.