In a domain environment, administrator can centrally configure Windows Firewall rule using Group Policy. This way, the rules will be automatically applied to all targeted computers in the domain and therefore increasing the security.
Rather than manually configuring Windows Firewall rules individually on each server, we can instead configure firewall rules for multiple profiles using group policy, allowing us to roll them out to a group of computers at once.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to perform related firewall queries.
In this context, we shall look into how to Configure Windows Firewall Rule using Group Policy.
How to Configure Windows Firewall Rule using Group Policy ?
Windows Firewall allows to restrict inbound/outbound network traffic for a certain application, protocol or a TCP/IP port.
This is an easy way to restrict network access to/from user workstations or servers.
Group Policy Settings to Manage Windows Defender Firewall Rules
There are two sections in the Group Policy Management console that allow you to manage firewall settings:
i. Firstly, computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Firewall – this GPO section was used to configure firewall rules in OS Vista/Windows Server 2008 or earlier.
If we do not have any computers with these old OS versions, use the next policy section to configure the firewall.
ii. Secondly, computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
How to Enable Windows Firewall Using GPO ?
It is recommended to configure the automatic startup of Windows Firewall using GPO.
i. To do it, go to Computer Configuration- > Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services.
ii. Find Windows Firewall in the list of services and change the startup mode to automatic (Define this policy setting -> Service startup mode Automatic).
iii. Make sure that the users do not have the permissions to stop the service.
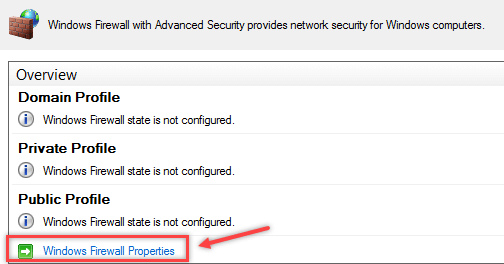
iv. Next, go to the Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings section in the GPO console. Right-click Windows Firewall with Advanced Security and open the properties.
v. Then, change the Firewall state to On (recommended) in all three tabs: Domain Profile, Private Profile and Public Profile.
vi. Later, depending on the security policies in the company, you can specify that all inbound connections are blocked by default and outbound connections are allowed.
vii. Finally, Save the changes.
How to Create a Firewall Rule Using GPO ?
The firewall rule wizard has an interface similar to that of local Windows Firewall on the user's desktop computer.
Select the rule type. We can allow access to:
- Program – we can select a program executable (.exe).
- Port – we can select a TCP/UDP port or a port range.
- Predefined – we can select one of the standard Windows rules, which already contain access rules (both executable files and ports are described) to typical services (for example, AD, HTTP(s), DFS, BranchCache, remote restart, SNMP, KMS, etc).
- Custom – here we can specify a program, a protocol (protocols other than TCP or UDP, like ICMP, GRE, L2TP, IGMP, etc), client IP addresses or entire IP subnets.
In this case , we will select the Port rule. Let us specify TCP as the protocol and Port 3389 as the port (it is the default RDP port, but we can change it via the registry).
Then, we must select what to do with such a network connection: Allow the connection, allow if it is secure or Block the connection.
Then, select the firewall profiles to apply the rule to. We can leave all profiles enabled (Domain, Private and Public).
Finally, specify the name and description of the rule. Click Finish and it will appear in the list of firewall rules.
In the same way, we can configure other rules for the inbound traffic to be applied to Windows clients.
Do not forget to create rules for the inbound and outbound traffic.
Then, just assign the Firewall Policy to the OU with user computers.
Before applying the firewall policy to OU with productive computers, it is strongly recommend to try it out on some test computers.
Otherwise, due to wrong firewall settings, we will be paralyzed. To diagnose how group policy is applied, use the gpresult tool.
Testing Windows Firewall Policies on Clients
Update the group policy settings on our clients (gpupdate /force). Make sure that the ports we have specified are available on user computers:
- On a user PC, open the Control Panel -> System&Security -> Windows Defender Firewall and make sure that there is the message 'For your security, some settings are controlled by Group Policy' and our firewall settings are used.
- Now a user cannot change firewall settings and all rules that we have created must appear in the Inbound Rules list.
- We can also display the firewall settings using this command:
- netsh firewall show state
How to Import/Export Windows Firewall Rules to/from GPO ?
Of course, the process of creating Windows Firewall rules is a painstaking and time consuming task (however, it is worth the effort):
- To make it easier, we can import/export Windows Firewall settings.
- To do it, it is enough to configure local firewall settings on a reference workstation as we need.
- Then, go to the root of Windows Firewall snap-in (Windows Firewall with Advanced Security) and select Action -> Export Policy.
- The policy will be exported into a WFW file, which can be imported to the Group Policy Management Editor by selecting Import Policy option and specifying the path to the .wfw file (the current policy settings will be overwritten).
Domain and Local Windows Defender Firewall Rules
Depending on whether we want that local administrators can create their own firewall rules on their computers to be combined with the rules obtained from the group policy, we can select the rule merging option:
- Firstly, open the policy properties and view the settings in the Rule merging section. By default, rule merging is enabled.
- We can force that a local administrator can create their own firewall rules: select Yes (default) in the Apply local firewall rules option.
Blocking firewall rules have higher priority than the allowing ones.
It means that a user cannot create an allowing access rule if it contradicts the blocking rule configured by an administrator using GPO.
However, a user will be able to create a local blocking rule, even if the access is allowed in the policy by the administrator.
Managing Windows Firewall with GPOs
Of course, we should create separate policies to manage Windows Firewall rules for servers and workstations.
It means that firewall rules for the domain controller, an Exchange mail server and an SQL server will differ.
We can find what ports must be opened for each service on the vendor's website.
The process is quite painstaking and complicated at the first glance.
However, we can finally get a working Windows Firewall configuration that allows only approved network connections and blocks other ones.
[Need help with configuring Windows Firewall Rule using Group Policy? We are here for you. ]
Conclusion
This article covers methods to Configure Windows Firewall Rule using Group Policy. Most of the procedures in this guide instruct you to use Group Policy settings for Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
To open a GPO to Windows Firewall with Advanced Security:
1. Open the Group Policy Management console.
2. In the navigation pane, expand Forest: YourForestName, expand Domains, expand YourDomainName, expand Group Policy Objects, right-click the GPO you want to modify, and then click Edit.
3. In the navigation pane of the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security - LDAP://cn={GUID},cn=
This article covers methods to Configure Windows Firewall Rule using Group Policy. Most of the procedures in this guide instruct you to use Group Policy settings for Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
To open a GPO to Windows Firewall with Advanced Security:
1. Open the Group Policy Management console.
2. In the navigation pane, expand Forest: YourForestName, expand Domains, expand YourDomainName, expand Group Policy Objects, right-click the GPO you want to modify, and then click Edit.
3. In the navigation pane of the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security - LDAP://cn={GUID},cn=