Are you having issues fixing high memory usage by Metafile on Windows Server 2008 R2?
This guide is for you.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to fix high memory usage by Metafile on Windows Server 2008 R2.
In this context, we shall look into the steps to fix memory usage issue.
More about High RAM Load on Windows Server 2008 R2?
Windows Server 2008 R2 is prone to face high RAM load which results in issues with the server and application performance.
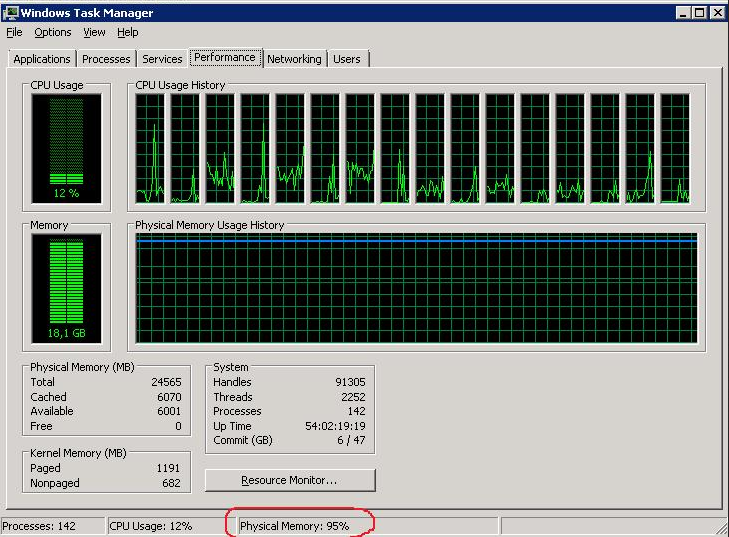
From the Task Manager, we sometimes see that physical memory is busy by 95-99%
And from the Processes tab, we will not be able to find any leaked process with abnormally high memory consumption.
When we sum up the approximate values of memory used by all processes we will not get even 50% of the physical memory we have on our server.
How to find the actual RAM usage?
To get the actual data on RAM usage we can use a small utility – RAMMap.
We have to download the archive containing the tool and run RAMMap.exe with the administrator privileges.
Then from the ‘Use Counts’ tab, we can see that Metafile is using the largest amount of RAM.
[Need urgent Assistance? We are here to help you!]
What is a Metafile ?
A metafile is a part of the system cache that contains NTFS metadata. Metafile increases the performance of the file system while accessing it.
NTFS metadata includes the data of MFT (Master File Table). Every time a file or folder is accessed by the users, a corresponding block of at least 1 KB is created in the metafile.
How to Quickly Clean Up metafile?
Windows Server 2008 R2 with too many files will have a large metafile size (NTFS cache)
There are two methods with which we can clean up metafile. Using either of the method will fix high memory usage by Metafile on Windows Server 2008 R2
i. Using RAMMap tool
ii. Dynamic Cache Service to Manage the File Cache
1. Clearing memory using RAMMap
RAMMap allows to clear the used memory quickly without server restart.
Select Empty -> Empty System Working Set in the menu.
We can see that the size of metafile in the memory reduces, and the percentage of RAM used by CPU drops from 95% to 26%.
2. Managing the File Cache with Dynamic Cache Service
This service allows us to manage the parameters of dedicated MFT cache using system APIs.
We need to download DynCache and then copy the file DynCache.exe to %SystemRoot%\System32 folder
Then we need to create DynCache service.
We can use the following command:
sc create DynCache binpath= %SystemRoot%\System32\DynCache.exe start= auto type= own DisplayName= “Dynamic Cache Service” install DynCache service
After adding the command we need to import DynCache.reg to the registry which ontains default values.
And then we have to change the values of the following register keys:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DynCache\Parameters
1. MaxSystemCacheMBytes: 4096 (dec) – the maximum cache size(Mb)
2. MinSystemCacheMBytes: 100 (dec) – the minimum cache size (MB)MaxSystemCacheMBytes
We need to keep in mind that DynCache service settings have to be edited according to the RAM size, the server load, required performance, etc.
After the changes are made, we do not need to restart DynCache, since all changes are applied dynamically.
Now we can run the service using this command:
sc start DynCache
After running Dynamic Cache Service we will be able to see that the memory usage in the server has decreased to a normal amount.
[Still facing high memory usage on your server? We are available to help you today!]
Conclusion
This guide will help you to fix high memory usage issue by Metafile on Windows Server 2008 R2.
This guide will help you to fix high memory usage issue by Metafile on Windows Server 2008 R2.