Are you trying to fix SSLRandomSeed cannot occur within VirtualHost section?
This guide is for you.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to fix VirtualHost related queries.
In this context, we shall look into the cause and fix of this error.
Nature of SSLRandomSeed cannot occur within VirtualHost section?
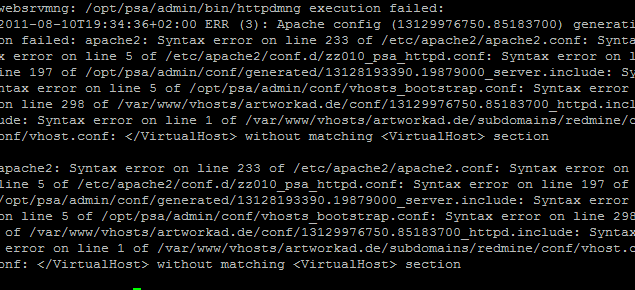
While we restart apache, we might receive the error:
# ./apachectl startssl
Syntax error on line 983 of /kit/conf/httpd.conf:
SSLRandomSeed cannot occur within <VirtualHost> section
../apachectl startssl: httpd could not be startedThis error occurs when the SSLRandomSeed directive is specified inside the VirtualHost section.
More about SSLRandomSeed directive ?
SSLRandomSeed directive configures one or more sources for seeding the Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG) in OpenSSL at startup time and/or just before a new SSL connection.
We can only use this directive in the global server context because the PRNG is a global facility.
The syntax of the SSLRandomSeed directive is given below:
SSLRandomSeed context source [bytes]The following source variants are available:
builtin
This is the always available builtin seeding source. Its usage consumes minimum CPU cycles under runtime.
The drawback is that at startup time this source just produces a few bytes of entropy. So we should always, at least for the startup, use an additional seeding source.
file:/path/to/source
This variant uses an external file /path/to/source as the source for seeding the PRNG.
When bytes are specified, only the first bytes number of bytes of the file form the entropy. When bytes are not specified the whole file forms the entropy.
We use this especially at startup time, for instance with available /dev/random and/or /dev/urandom devices.
However, /dev/random provides only as much entropy data as it actually has, i.e. when we request 512 bytes of entropy, but if the device has only 100 bytes available two things can happen: On some platforms, we receive only the 100 bytes while on other platforms the read blocks until enough bytes are available.
Here using an existing /dev/urandom is better, because it never blocks and actually gives the amount of requested data. The drawback is just that the quality of data may not be the best.
exec:/path/to/program
This variant uses an external executable /path/to/program as the source for seeding the PRNG.
When bytes is specified, only the first bytes number of bytes of its stdout contents form the entropy. When bytes are not specified, the entirety of the data produced on stdout forms the entropy.
We use this only at startup time when we need a very strong seeding with the help of an external program. Using this in the connection context slows down the server too dramatically. So usually we should avoid using external programs in that context.
egd:/path/to/egd-socket (Unix only)
This variant uses the Unix domain socket of the external Entropy Gathering Daemon (EGD) to seed the PRNG. We use this if no random device exists on our platform.
For example:
SSLRandomSeed startup builtin
SSLRandomSeed startup “file:/dev/random”
SSLRandomSeed startup “file:/dev/urandom” 1024
SSLRandomSeed startup “exec:/usr/local/bin/truerand” 16
SSLRandomSeed connect builtin
SSLRandomSeed connect “file:/dev/random”
SSLRandomSeed connect “file:/dev/urandom” 1024How to fix SSLRandomSeed cannot occur within VirtualHost section ?
In order to fix this error, an effective method is to move the SSLRandomSeed directives higher up in the conf file, before the VirtualHost sections.
It will be better to specify directly under the <IfDefine SSL> or prior to that.
[Still facing this SSL Apache error? We can help you fix. ]
Conclusion
This article will guide you on how to fix SSLRandomSeed cannot occur within VirtualHost section which triggers when the #SSLRandomSeed directive is specified inside the #VirtualHost section.
This article will guide you on how to fix SSLRandomSeed cannot occur within VirtualHost section which triggers when the #SSLRandomSeed directive is specified inside the #VirtualHost section.