Are you trying to control bounce back email messages?
This guide will help you.
Often, we may send emails and they might fail to reach the recipient’s inbox. This condition is email bounce back.
If this is the case, then the email service provider sends an email bounce back messages about failed delivery and technical details of the failure.
In some other cases, the server might be flooded with these messages. It might be as a result of spamming or spoofing attacks.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to configure their email servers to prevent spamming attacks.
In this context, we shall look into ways to control bounce back email messages.
What triggers Bounce back email messages ?
Emails can bounce back due to several reasons which include:
i. Invalid or nonexistent email address
ii. Blocked sender’s IP address
iii. Email blocked by receiving server
iv. Receiving server is overloaded
v. The receiver's inbox is full
vi. Low sender reputation score
vii. The recipient has added an auto-reply
viii. Email size is too large
Methods to control bounce back email messages ?
It is a common incident that our server will be flooded with bounce back emails and we are not able to find the exact problem. In such cases, there are two possible causes for these bounce back messages:
i. Spamming
ii. Spoofing
Let us discuss them in details. Also, we will provide some examples and solutions.
1. Spamming
Generally, spamming occurs mainly in two forms.
Case 1:
Here, the email account will compromise and the hacker will send spam emails from the account. The mails to non-existent email accounts will bounce back.
To confirm this, we need to check the mail logs first.
We use the "exigrep" command and check the Exim mail log "/var/log/exim_mainlog".
From the mail transaction details, we will find how the mails were sent:
#exigrep test@sample.com /var/log/exim_mainlog | head -100This command will take the first 100 lines of the mail log of the mail account test@sample.com.
Please note that test@sample.com is a sample mail account.
Here is a sample email transaction from the Exim log:
———————–
2021-02-03 13:13:21 1TJVJp-0004Ns-Pr <= test@sample.com H=(sample.com) [1.1.1.1]:46779 P=esmtpa A=courier_login:test@sample.com S=616 id=2956633080.20121003171321@sample.com T=”oooooooooV,-,1,-,A,-,G,-,R,-,Aooooooooo” for test@yahoo.com 2012-10-03 13:13:21 1TJVJp-0004Ns-Pr SMTP connection outbound 1349295201 1TJVJp-0004Ns-Pr sample.com test@yahoo.com
———————–On analyzing the log, we can see that the email was sent from the address “test@sample.com” with proper authentication using the same email account.
A=courier_login:test@sample.com
This indicates that the account is compromised and the hacker has access to this email account.
In order to resolve this, we have to reset the password of the email account. Before proceeding, we use the below command to delete the spam mails present in the mail queue:
#exiqgrep -i -f test@sample.com | xargs exim -MrmThis command removes all the mails that are sent from this mail address (which are currently present in the queue):
#exiqgrep -i -r test@sample.com | xargs exim -MrmThis command removes all the emails received to this email address (which are present in the queue).
Case 2:
In the second type of spamming, the email account will compromise, and emails are sent after spoofing.
For example, we can check the below log:
——————-
2021-02-03 13:13:21 1TJVJp-0004Ns-Pr <= 12344@choco.com H=() [1.1.1.1]:46779 P=esmtpa A=courier_login:test@sample.com S=616 id=2956633080.20121003171321@sample.com T=”oooooooooV,-,1,-,A,-,G,-,R,-,Aooooooooo” for test@yahoo.com 2012-10-03 13:13:21 1TJVJp-0004Ns-Pr SMTP connection outbound 1349295201 1TJVJp-0004Ns-Pr sample.com test@yahoo.com
——————-From the log, we can see that the mails are gone from the email address 12344@choco.com. However, we cannot find such an email account on the server.
Since the login occurs to be the test@sample.com, but the mails are gone as 12344@choco.com we can ensure test@sample.com is compromised and then sent mails after spoofing.
In this case, also, reset the password of test@sample.com and clear the mail queue as we did above.
2. Spoofing
If we are not able to see any details that the mail is sent from the server when we check the Exim logs, it will usually be a spoofing activity.
The mails sent through spoofing does not pass through our server in any way, but the bounce back messages will come back to the mailbox on our server.
However, in this case, the email account will not compromise.
There is no effective way to prevent spoofing from our end. The only thing we can do is, set up an SPF record for the domain with only our IPs allowed to send mails using this domain.
This may not prevent spoofing, but if the recipient mail server checks the SPF record of the incoming emails, then the spoofed emails will not deliver to the recipient.
In this case, also, there will be a bounce-back message to the email account. We can add filtering rules from Cpanel to filter out such emails.
[Failed to control bounce back emails? We can help you. ]
Conclusion
This article will guide you on how to control #bounce back #email #messages. Email bounce back is the condition when emails fail to reach the recipient’s inbox.
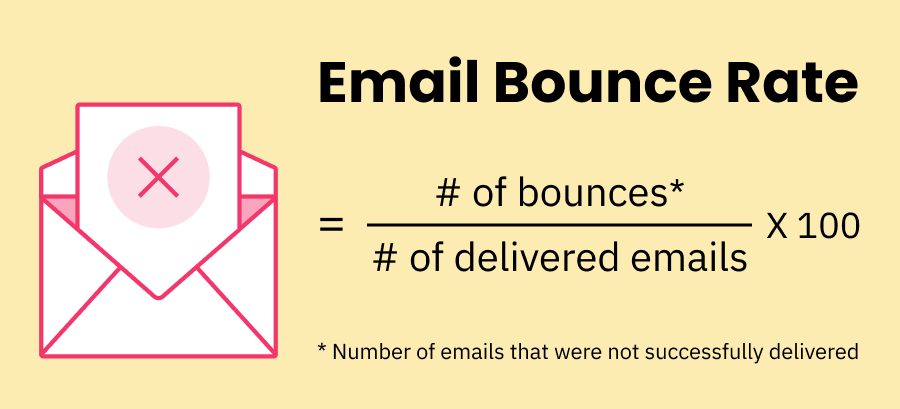
The accepted benchmark for bounced emails is 2%. This means for every 100 emails you send, two will be returned to you. Often times, your bounce rate will be much lower. Anything between 2% and 5% is worth noting.
On average maintaining a lower bounce rate is an essential part of your SEO. Normally, your bounce rate should be between 26% - 70%. On average you should maintain between 41% - 55%. However, if you could lower it down to 26% - 40% that's excellent.
To Reduce Email Bounce Rate:
1. Only Use Permission-Based (Opt-In) Email List.
2. Keep Your Subscribers' List Updated.
3. Don't Use Your First Campaign As A Way To 'Clean' Your List!
4. Verify The Email Addresses.
5. Be Consistent With Your Emails.
6. Write Quality Emails.
7. Avoid Creating Spam-Like Emails.
8. Do Not Use Free #Sender #Domains.
This article will guide you on how to control #bounce back #email #messages. Email bounce back is the condition when emails fail to reach the recipient’s inbox.
The accepted benchmark for bounced emails is 2%. This means for every 100 emails you send, two will be returned to you. Often times, your bounce rate will be much lower. Anything between 2% and 5% is worth noting.
On average maintaining a lower bounce rate is an essential part of your SEO. Normally, your bounce rate should be between 26% - 70%. On average you should maintain between 41% - 55%. However, if you could lower it down to 26% - 40% that's excellent.
To Reduce Email Bounce Rate:
1. Only Use Permission-Based (Opt-In) Email List.
2. Keep Your Subscribers' List Updated.
3. Don't Use Your First Campaign As A Way To 'Clean' Your List!
4. Verify The Email Addresses.
5. Be Consistent With Your Emails.
6. Write Quality Emails.
7. Avoid Creating Spam-Like Emails.
8. Do Not Use Free #Sender #Domains.