Need to know more about KVM hypervisor ?
This is the guide.
Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is an open source virtualization technology built into Linux. Specifically, KVM lets you turn Linux into a hypervisor that allows a host machine to run multiple, isolated virtual environments called guests or virtual machines (VMs).
You might be wondering if Linux and Windows virtual machines run side by side on the same hardware.
The fact is that it is possible using KVM virtualization. And, KVM hypervisor is the main factor that makes this virtualization possible.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to perform Virtualization related tasks.
In this context, we shall look into on how the KVM hypervisor works.
Nature of KVM and hypervisor ?
Virtualization allows us to use a physical machine’s full capacity by distributing its capabilities among many users or environments.
And, it can increase IT agility, flexibility, and scalability while creating significant cost savings. And, KVM is one of the best virtualization techniques.
KVM Virtualization is a leading open-source complete virtualization solution. It supports all major operating systems including Linux and Windows.
And, it allocates separate virtual computing resources for each virtual machine such as the processor, storage, memory, etc.
Now, have any idea about how does KVM hypervisor support this virtualization?
More about Hypervisor ?
Basically, the functions of the hypervisor enable virtualization.
So, the function of partitioning, abstracting, and isolating different OS and applications from the underlying computer hardware is what the hypervisor does.
Also, hypervisor helps manage independent Virtual Machines by distributing hardware resources such as memory allotment, CPU usage network bandwidth, and more amongst them.
In short, hypervisor helps VMs to connect with one another.
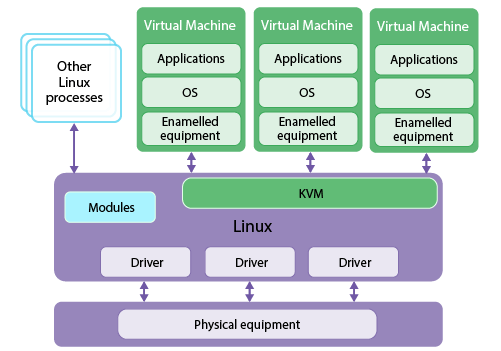
How KVM hypervisor works?
Basically, there are mainly two types of hypervisors. Type 1 or Native hypervisor and Type 2 or hosted hypervisor.
Type 1 hypervisors run on the host machine’s hardware directly. This means the hypervisor has direct hardware access without contending the OS.
And, Type 2 hypervisors rely on top of operating systems. Because of this reason, these are known as Hosted hypervisors.
Also, it supports multiple guest machines but cannot directly access host hardware and its resources.
And, KVM has a unique hypervisor that has the characteristics of both Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors.
[Need more information related to Hypervisor?- We're available 24/7. ]
Conclusion
This article will guide you on how the KVM #hypervisor works. Basically, KVM is a type-2 hypervisor (installed on top of another OS, in this case some flavor of #Linux).
It runs, however, like a type-1 hypervisor and can provide the power and functionality of even the most complex and powerful type-1 hypervisors, depending on the tools that are used with the KVM package itself.
KVM (for Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a full virtualization solution for Linux on x86 hardware containing virtualization extensions (Intel VT or AMD-V).
Using KVM, one can run multiple virtual machines running unmodified Linux or Windows images.
1. The main difference between Type 1 vs. Type 2 hypervisors is that Type 1 runs on bare metal and Type 2 runs on top of an operating system.
2. Each hypervisor type also has its own pros and cons and specific use cases.
3. Xen is better than #KVM in terms of virtual storage support, high availability, enhanced security, virtual network support, power management, fault tolerance, real-time support, and virtual CPU scalability.
4. A Type 1 hypervisor takes the place of the host operating system.
5. Type 1 hypervisors are highly efficient because they have direct access to physical hardware.
6. This also increases their security, because there is nothing in between them and the CPU that an attacker could compromise.
This article will guide you on how the KVM #hypervisor works. Basically, KVM is a type-2 hypervisor (installed on top of another OS, in this case some flavor of #Linux).
It runs, however, like a type-1 hypervisor and can provide the power and functionality of even the most complex and powerful type-1 hypervisors, depending on the tools that are used with the KVM package itself.
KVM (for Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a full virtualization solution for Linux on x86 hardware containing virtualization extensions (Intel VT or AMD-V).
Using KVM, one can run multiple virtual machines running unmodified Linux or Windows images.
1. The main difference between Type 1 vs. Type 2 hypervisors is that Type 1 runs on bare metal and Type 2 runs on top of an operating system.
2. Each hypervisor type also has its own pros and cons and specific use cases.
3. Xen is better than #KVM in terms of virtual storage support, high availability, enhanced security, virtual network support, power management, fault tolerance, real-time support, and virtual CPU scalability.
4. A Type 1 hypervisor takes the place of the host operating system.
5. Type 1 hypervisors are highly efficient because they have direct access to physical hardware.
6. This also increases their security, because there is nothing in between them and the CPU that an attacker could compromise.