Need to know the Advantages of SAN over NAS?
This guide is for you.
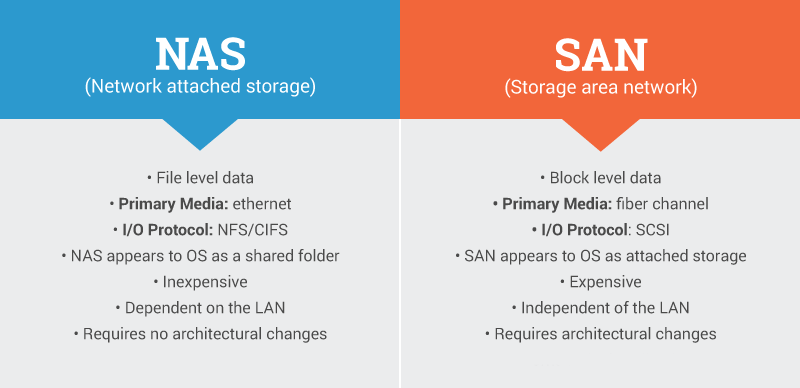
Network-attached storage (NAS) and Storage area network (SAN) were developed to solve the problem of making stored data available to a lot of users at once.
Each of them provides dedicated storage for a group of users.
SAN and network-attached storage (NAS) are both network-based storage solutions.
A SAN typically uses Fibre Channel connectivity, while NAS typically ties into to the network through a standard Ethernet connection.
A SAN stores data at the block level, while NAS accesses data as files.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to handle disk and storage related issues.
In this context, we shall look into the Advantages of SAN over NAS.
More about NAS and SAN?
NAS is a data storage device connected to a network providing data access to clients. At its base, it is built with either SAS or SATA disks arranged in a RAID and it is then attached to devices over ethernet.
Above all, NAS is a highly specialized file server and because of its hardware, software, or specific configuration, NAS only does storage.
SAN is a dedicated network that enables servers to share a pool of storage resources. SANs are complex, interwoven systems with mission-critical data and databases.
Advantages of SAN over NAS ?
1. High performance
A SAN other devices in the network will not have to use local storage. Thus, allowing them to run more smoothly. When the server rarely or never uses internal hard drives it will naturally consume less power and run at a cooler temperature.
2. Fast backup
One can take more rapid backups when the client OSs see the SAN as attached storage. The transparency of SAN to the client OS allows storing data quickly. As it is an entirely distinct network, SANs do not cause any bottlenecks as other storage solutions do at times.
3. Disaster recovery
SAN makes it easy for replicating data from the primary locations to an offsite. It helps us to replicate rapidly and get our environment up and running quickly. As a result, we will not get many downtimes.
4. Better redundancy
Since the servers within the SAN function as one cluster, you are not necessarily accessing one particular device. If one of the servers goes down, the other devices within the same network pick up the slack. Such a high level of redundancy is unparalleled by any other storage solution.
5. Scalability
Entry-level and NAS devices are not highly scalable, but high-end NAS systems scale to petabytes using clusters or scale-out nodes. In contrast, scalability is a major driver for purchasing a SAN. Its network architecture enables admins to scale performance and capacity in scale-up or scale-out configurations.
6. Extremely fast data access
SAN makes it easy for us to access data very fast.
7. Dedicated network for storage relieves stress on LAN
When we have a dedicated network like that of SAN there will not be much pressure on LAN regarding the storage space.
8. OS-level access to files
SAN allows us to access files at block-level or OS level.
9. High quality-of-service for demanding applications
Applications such as the video editing ones get simultaneous access to the cache thus benefiting them from not getting network traffic bottlenecks.
10. Typically used in professional and enterprise environments.
Storage area networks are more always chosen over NAS.
11. Improves Disk Utilization.
The primary advantage of using a Storage Area Network (SAN) is improving disk utilization.
Moreover, centralizing storage availability allows managing everything easily.
[Need urgent assistance to install Software on Ubuntu Server? We are available to help you. ]
Conclusion
This article covers more insight about the advantages of SAN over NAS.
A storage area network (#SAN) is a dedicated, independent high-speed network that interconnects and delivers shared pools of storage devices to multiple servers. Each server can access shared storage as if it were a drive directly attached to the server.
Network Attached Storage (#NAS) is a device that allows users to access files through a network. It allows users to access and share files from their individual stations through a central server. NFS (Network File System) is a protocol that is used to serve and share files on a network.
Some advantages of a SAN:
1. Reduces LAN bandwidth problems. A key benefit of SANs is bandwidth improvement. 2. Improved data security. Data security is paramount for every business.
3. Responsive backup.
4. Increased scalability.
5. Reliable disaster recovery.
What is the purpose of a SAN?
SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage.
A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
This article covers more insight about the advantages of SAN over NAS.
A storage area network (#SAN) is a dedicated, independent high-speed network that interconnects and delivers shared pools of storage devices to multiple servers. Each server can access shared storage as if it were a drive directly attached to the server.
Network Attached Storage (#NAS) is a device that allows users to access files through a network. It allows users to access and share files from their individual stations through a central server. NFS (Network File System) is a protocol that is used to serve and share files on a network.
Some advantages of a SAN:
1. Reduces LAN bandwidth problems. A key benefit of SANs is bandwidth improvement. 2. Improved data security. Data security is paramount for every business.
3. Responsive backup.
4. Increased scalability.
5. Reliable disaster recovery.
What is the purpose of a SAN?
SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage.
A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).