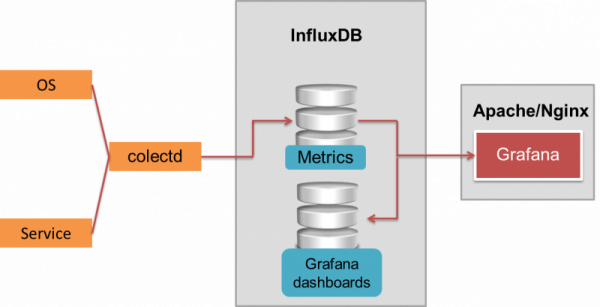
Are you trying to install InfluxDB on CentOS 7 ?
This guide is for you.
InfluxDB is a time series database designed to handle high write and query loads. Open source server agent to collect metrics from stacks, sensors and systems.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to perform Software Installation tasks on their Linux Servers.
In this context, we shall look into steps to Install InfluxDB on Linux.
More information about InfluxDB
InfluxDB allows us to store a huge volume of time-series data.
Advantages of using InfluxDB can be considered from its scalability to the simple query syntax it has along with the advantage of not using any external dependencies.
It is basically a time series, metrics, and analytics database. It contains data such as system metrics and application metrics.
Here, you will learn how to install InfluxDB, a real-time powerful monitoring framework that provides a historical analysis can be made using InfluxDB.
InfluxDB organizes data on disk into immutable runs of values for a single column of a series. InfluxDB now includes Flux, a powerful language that allows developers to see across time.
We will need a 64-bit CentOS 7 server with a sudo non-root user along with 4GB swap space, and at least a 2GB RAM and 2 procs as prerequisites.
The following are the steps taken to do this setup.
1. Installing and configuring InfluxDB
i. We can use the following commands to install InfluxDB first.
$ sudo yum -y update
$ sudo yum -y install https://s3.amazonaws.com/influxdb/influxdb-latest-1.x86_64.rpmii. For disabling anonymous data reporting and extending the read-timeout limit we will customize the InfluxDB configuration after taking a backup of the original conf file.
$ sudo cp /opt/influxdb/shared/config.toml /opt/influxdb/shared/config.toml_backupiii. Then we will minimize the bandwidth usage by disabling reporting, as InfluxDB reports anonymous data once every 24 hours.
$ sudo nano /opt/influxdb/shared/config.tomlChange 'reporting-disabled' to true
reporting-disabled = trueiv. . After that we will increase the default read-timeout slightly.
$ sudo nano /opt/influxdb/shared/config.toml
read-timeout = "10s"v. We can save and close the file, then start the InfluxDB daemon.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/influxdb startvi. Now we can take a browser and check http://server_ip:8083 to see if InfluxDB is up and running.
[InfluxDB not running on your Server? We can help you!]
2. Changing the Default InfluxDB Admin Credentials
i. To change the default InfluxDB admin credentials we will log into the InfluxDB UI using the default username 'root' and password 'root' in the Connect section.
ii. And click the Connect button leaving the database portion blank.
iii. From the top menu on the next page, click on Cluster Admins.
iv. In the Username section, we have to click on root and change the password.
v. Then click the Change Password button after providing the desired password.
vi. Finally, log out by clicking the Disconnect button, and try logging in with the newly set credentials.
3. Database Creation
Here we will create a database to store our metrics.
The steps to follow are given below:
i. First, click on the Databases menu from the top menu in the web UI.
ii. Under Database Details in the Create a Database section, we will enter metrics as the database name.
iii. We will keep the default options available in ‘Shared Spaces’ and click the Create Database button to create the database.
Once this is database is successfully created we can see it listed at the top of the screen next to the Explore Data link.
[Need urgent assistance for any Linux related Software Installation? We are happy to help you! ]
Conclusion
This article will guide you on steps to Install #InfluxDB on #CentOS 7. You can Turn any InfluxData #instance into a production-ready cluster that can run anywhere. Easily create and share a comprehensive monitoring solution.
InfluxDB is similar to a #SQL #database, but different in many ways. Relational databases can handle time series data, but are not optimized for common time series workloads. InfluxDB is designed to #store large volumes of time series data and quickly perform real-time analysis on that data.
The local InfluxDB configuration file is located here: Linux: /etc/influxdb/influxdb. conf. macOS: /usr/local/etc/influxdb.
To Install InfluxDB:
Option 1 : Download the InfluxDB archive via the browser.
Option 2 : Adding the #repositories to your package manager.
i – Start your InfluxDB service.
ii – Configure your InfluxDB instance.
iii – Test your InfluxDB instance.
iv – #Download InfluxDB 2.0 archive from the website.
This article will guide you on steps to Install #InfluxDB on #CentOS 7. You can Turn any InfluxData #instance into a production-ready cluster that can run anywhere. Easily create and share a comprehensive monitoring solution.
InfluxDB is similar to a #SQL #database, but different in many ways. Relational databases can handle time series data, but are not optimized for common time series workloads. InfluxDB is designed to #store large volumes of time series data and quickly perform real-time analysis on that data.
The local InfluxDB configuration file is located here: Linux: /etc/influxdb/influxdb. conf. macOS: /usr/local/etc/influxdb.
To Install InfluxDB:
Option 1 : Download the InfluxDB archive via the browser.
Option 2 : Adding the #repositories to your package manager.
i – Start your InfluxDB service.
ii – Configure your InfluxDB instance.
iii – Test your InfluxDB instance.
iv – #Download InfluxDB 2.0 archive from the website.