Are you trying hard to mitigate ICMP Flood Attack?
This guide will help you.
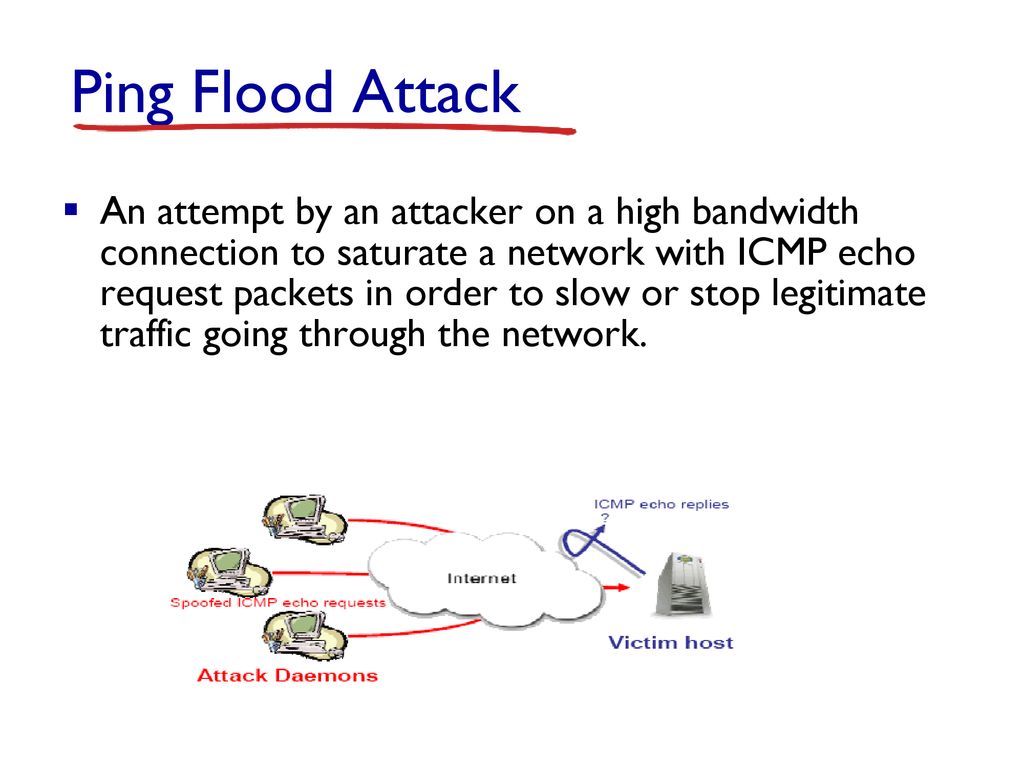
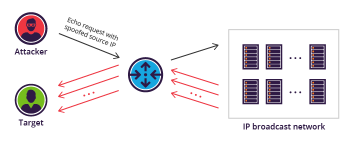
An Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) flood DDoS attack, also known as a Ping flood attack, is a common Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack in which an attacker attempts to overwhelm a targeted device with ICMP echo-requests (pings).
When the attack traffic comes from multiple devices, the attack becomes a DDoS attack.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to fix DDoS related attacks.
In this context, we shall look into how to mitigate this DDoS attack.
Nature of Ping flood attack or ICMP Flood Attack ?
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) utilized during a Ping Flood attack, is an internet layer protocol used by network devices to communicate with each other.
Generally, ICMP uses echo-request and echo-reply messages to ping a network device.
This is for checking the health and connectivity of the device and the connection between the sender and the device.
An ICMP request requires some server resources to process each request and to send a response.
The request also requires bandwidth on both the incoming message (echo-request) and outgoing response (echo-reply).
The Ping Flood attack influences the targeted device’s ability to respond to the high number of requests.
This, in turn, overloads the network connection with huge traffic.
The DDoS form of a Ping (ICMP) Flood can be split into the following steps:
i. Attacker sends many ICMP echo request packets to the target server using multiple devices.
ii. The targeted server then sends an ICMP echo reply packet to each requesting device’s IP address as a response.
The damaging effect of a Ping Flood is directly proportional to the number of requests made to the targeted server.
Ping Flood attack traffic is symmetrical.
Tips to mitigate ICMP Flood Attack?
Following are tips you can apply to mitigate ICMP flood attack.
1. Disabling ICMP functionality
Firstly we can try disabling a ping flood can be accomplished by disabling the ICMP functionality of the targeted router, computer, or other devices.
We can do this by accessing the administrative interface of the device and disable its ability to send and receive any requests using the ICMP.
We must keep in mind that all network activities involving ICMP will get disabled. This will make the device unresponsive to ping requests, traceroute requests, and other network activities.
2. Limiting the processing of incoming ICMP messages
Another approach to combating ICMP attacks is to rate-limit the processing of incoming ICMP messages.
This can be commonly done using Iptables. Here we will set 1 ping per second as it is plenty for legitimate uses.
We can use the following commands:
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type address-mask-request -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type timestamp-request -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type 8 -m limit --limit 1/second -j ACCEPT[Need urgent assistance to resolve DDoS attacks? We are happy to help you. ]
Conclusion
This article will guide you on methods to mitigate ICMP flood #attack. This is the type of Denial of Service (DoS) attack in which an attacker attempts to crash, destabilize, or freeze the targeted computer or service by sending malformed or oversized packets using a simple ping command.
Many network administrators feel that ICMP is a security risk, and should therefore always be blocked at the firewall. It is true that ICMP does have some security issues associated with it, and that a lot of #ICMP should be blocked.
But this is no reason to block all ICMP traffic!
To mitigate Ping flood attack:
1. Disabling a ping flood is most easily accomplished by disabling the ICMP functionality of the targeted router, computer or other device.
2. A network administrator can access the administrative interface of the device and disable its ability to send and receive any requests using the ICMP, effectively eliminating both the processing of the request and the Echo Reply.
3. The consequence of this is that all network activities that involve ICMP are disabled, making the device unresponsive to ping requests, traceroute requests, and other network activities.
This article will guide you on methods to mitigate ICMP flood #attack. This is the type of Denial of Service (DoS) attack in which an attacker attempts to crash, destabilize, or freeze the targeted computer or service by sending malformed or oversized packets using a simple ping command.
Many network administrators feel that ICMP is a security risk, and should therefore always be blocked at the firewall. It is true that ICMP does have some security issues associated with it, and that a lot of #ICMP should be blocked.
But this is no reason to block all ICMP traffic!
To mitigate Ping flood attack:
1. Disabling a ping flood is most easily accomplished by disabling the ICMP functionality of the targeted router, computer or other device.
2. A network administrator can access the administrative interface of the device and disable its ability to send and receive any requests using the ICMP, effectively eliminating both the processing of the request and the Echo Reply.
3. The consequence of this is that all network activities that involve ICMP are disabled, making the device unresponsive to ping requests, traceroute requests, and other network activities.