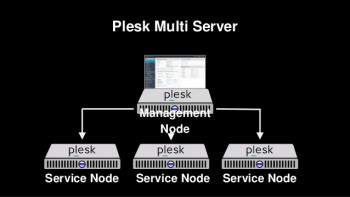
Plesk Multi Server How to install it
This article will guide you on how to install #Plesk #Multi #Server which will enable us to work with a single Plesk user interface to run hosting services on multiple #servers. A multi-server environment can support more #connections and services, helps to keep the system running, and can also cost significantly less each month than continually adding resources to a single server.
Plesk Multi Server is most useful for the following types of business:
1. Web design and development studios that also host the clients web sites;
2. Small and medium-sized shared hosting providers;
3. Larger hosting providers for #reselling to customers, who are small and medium-sized shared #hosting #providers.
Apache Performance Tuning via MPM Directives
This guide will help you to configure #MPM directives in the #Apache server. You can simply configure MPM #directives by logging into the server and create an optimization file and add the necessary directive change.
Starting with Apache 2.0, Apache extended its features with a selection of Multi-Processing Modules (#MPMs), which are responsible for binding to #network ports on the machine, accepting and handling the requests. These modules determine the basis of how Apache addresses multi-processing.
To know which MPM Apache is using:
1. Enable Apache mod_info.
2. Query the mod_info url, typically curl localhost/server-info.
3. The "Server Settings" section will show "MPM Name: #Worker"
4. Run httpd -V again. It will still show prefork, not worker.
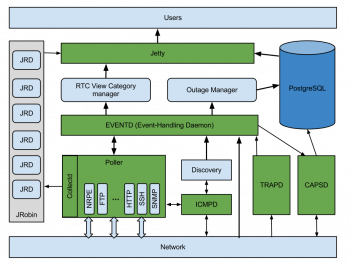
How to Install OpenNMS on CentOS 8
This article will guide via a step-by-step procedure to #install OpenNMS in #CentOS.
OpenNMS is a free, Open Source network monitoring system that can be used to #monitor tens of thousands of unlimited devices with a single #instance.
It will discover and monitor the services or nodes automatically in your #network, or you can assign a particular service to monitor by OpenNMS.
To configure #OpenNMS:
1. Install OpenNMS Horizon. Add yum repository and import GPG key.
2. Initialize and set up #PostgreSQL. Initialization of the PostgreSQL database will start.
3. Initialize and start OpenNMS Horizon.
4. First Login and change default password.
How to Install Python on Windows
This article will guide you on steps to install #Python and #PIP on #Windows. If you would like to download and install Python on your #computer you can do for free at python.org.
To install Python on Windows:
1. Select Version of Python to #Install.
2. Download Python Executable #Installer.
3. Run Executable Installer.
4. Verify Python Was Installed On Windows.
5. Verify Pip Was Installed.
6. Add Python #Path to #Environment Variables which is Optional.
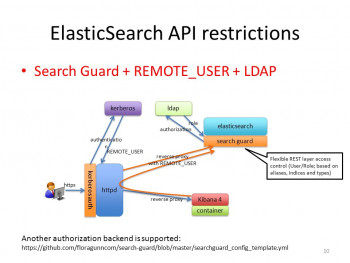
ElasticSearch LDAP Authentication on the Active Directory
This article will guide you on how to authenticate #ElasticSearch users using the Active Directory from #Microsoft #Windows and the #LDAP protocol.
#Active #Directory (#AD) supports both Kerberos and LDAP – Microsoft AD is by far the most common directory services system in use today.
To Set up Active Directory Authentication using LDAP:
1. Enter the LDAP "Server" and "Port" attributes on the Server Overview tab of the LDAP Users page.
2. Enter the proper base for the Active Directory in the "Base DN" attribute.
3. Set the Search Scope.
4. Enter the Username Attribute.
5. Enter the Search Filter.
6. Verify that the #settings are correct by clicking the Verify button.
Steps to Back Up And Restore Nagios System
This article will guide you on how to perform #Backup and #Restore of the #Nagios System are important aspects of the #administration and #maintenance of the #system.
Backups are an important aspect of administration and maintenance of your system. They can easily facilitate the #migration of a Nagios XI #installation between a virtual server and physical server, and the design of a fail-over or #disaster #recovery instance of Nagios XI.
There are three main types of backup: full, incremental, and differential:
1. #Full backup. As the name suggests, this refers to the process of copying everything that is considered important and that must not be lost.
2. #Incremental backup.
3. #Differential backup.